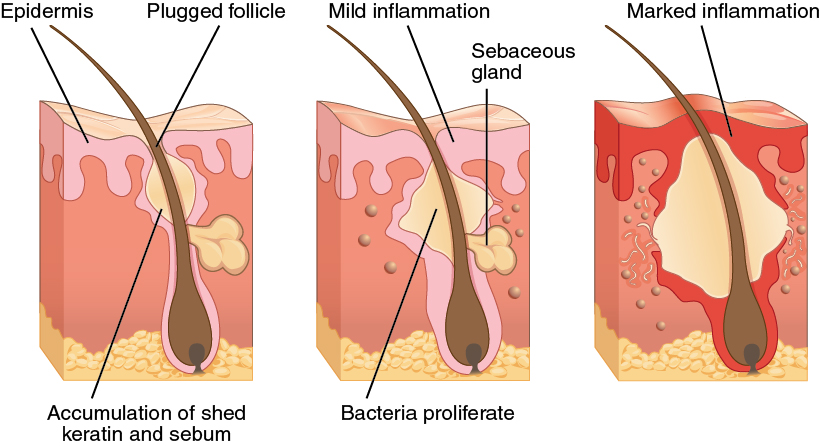
Acne
Adolescent F presents with gradual appearance of comedones, papules/pustules, and nodules on face. Denies use of androgens/steroids, isoniazid, lithium, phenytoin (Dilantin). Non-inflammatory nodules, inflamed comedones, and nodules noted on face, back.
Treatment
Stage 1
Noninflamed (blackheads and whiteheads)
Apply topical tretinoin 0.025% gel to acne lesions daily at bedtime
Stage 2
Inflamed comedones with few papules/pustules (pimples)
Apply benzoyl peroxide 10% gel sparingly twice daily; reduce frequency to once daily if excessive skin dryness occurs
Stage 3
Nodular lesions
Apply thin film of topical erythromycin 2.0% gel BID
Stage 4 refractory nodular/scarring acne: Start oral isotretinoin 1.0 mg/kg/day x 20 weeks and require pt
Enroll in iPLEDGE program
Obtain CBC, CMP, and fasting lipid panel
Obtain negative pregnancy test before starting medication and before each refill
Use two forms of birth control before engaging in sexually activity
Female: Consider combined oral contraceptives at any stage for improved acne control
Refractory acne: Refer to dermatology
Counseling
Pt counseled that acne is caused by bacterial infection with P. acnes
Pt informed that a minimum of 6-8 weeks is required to assess effectiveness of any one therapy
Pt advised that laser and light therapies are ineffective
Pt counseled that failure to comply with treatment may lead to continue acne and/or scarring
Notes
Rule out drug induced acne which may be caused by androgens/steroids, isoniazid, lithium, phenytoin (Dilantin)
Tretinoin = vitamin A derivative
Benzoyl peroxide (topical antiseptic)
Reduces risk for bacterial resistance when used with antibiotics
Pt may stop daily use once symptoms are controlled
Isotretinoin
Provider and pharmacy must be registered with iPLEDGE
Results
Long term remission in 40% of patients
40% of patients controlled with topical therapy after course
20% require re-treatment with isotretinoin