First Trimester Bleeding
Implantation Bleeding
Subchorionic Hemorrhage
Patient with h/o positive pregnancy test presents with first trimester bleeding. No vaginal, cervical, or hemorrhoid bleeding noted on exam.
U/S shows embryonic cardiac activity, blood present between chorion and uterine wall
Patient informed that risk for spontaneous abortion is 9% given presence of cardiac activity
Schedule for f/u in 1 week
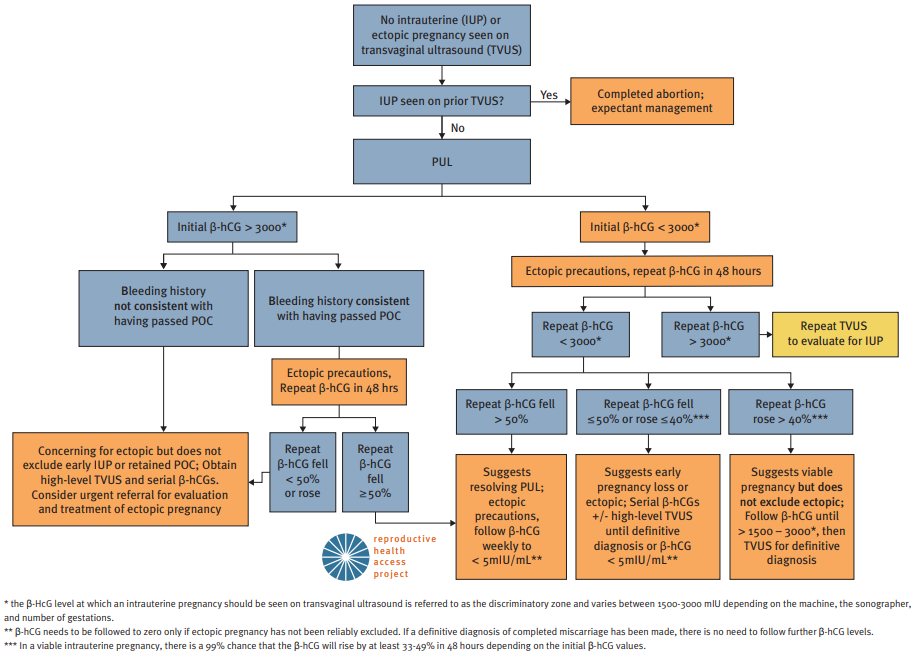
Initial evaluation of First Trimester Bleeding in Pregnancy of Unknown Location (PUL). Source: www.reproductiveaccess.org. Diagnosis and treatment algorithm is also available through the Reproductive Health Access Project.
Ectopic Pregnancy
Patient with h/o previous ectopic pregnancy, smoking, pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), and tubal surgery presents with abdominal pain and bleeding. LMP 6 weeks ago with IUD in place. No adnexal tenderness, rebound tenderness, cervical motion tenderness, or tissue lacerations. No products of conception present on speculum exam.
Obtain urine pregnancy test, CBC, blood type, and Rh status
Initial beta-hCG > 1500 mIU and increased < 50% after 48 hours
Trans-vaginal ultrasound (TVUS)
Failed to visualize intrauterine gestational sac and/or embryonic pole
Adnexal mass present
Treatment
Rh negative: Administer RhoGam
Medically stable: Discuss expectant management vs. methotrexate termination
Repeat beta-hCG in 4 to 7 days to ensure decrease of 15%
Failure of beta-hCG to decrease by 15%: Refer for surgical intervention
Ongoing pelvic pain, unstable vital signs, signs of intraperitoneal bleeding and/or failure of medical management: Refer for laparoscopic surgical intervention
Notes
Affects 1-2% of pregnancies
Major risk factors include previous tubal surgery (OR 21.0), previous ectopic pregnancy (OR 8.3), IUD (OR 5.0), h/o PID (OR 3.4), and smoking (OR 1.7-3.9)
Physical exam
Ectopic pregnancies often bleed even though they are not ruptured.
Rebound abdominal pain or cervical motion tenderness may indicate hemoperitoneum (surgical emergency)
Beta-hCG
Increases by 50% in 48 hours in 99% of viable pregnancies
For values >1500 mIU, an intrauterine pregnancy should be visible on U/S (note that the flow chart below uses >3000 mIU as a threshold)
For values <1500 mIU, repeat beta-hCG every 48 hours until a trend is established
For intrauterine pregnancies, TVUS should visualize a gestational sac with a yolk sac by 6 WGA
Consider laparoscopy if diagnosis is not clear within 10 days
Gestational Trophoblastic Disease
Pt with presents with first trimester bleeding. No vaginal, cervical, or hemorrhoid bleeding noted on exam.
Obtain baseline beta-hCG, CBC, CMP, TSH
U/S showing snowstorm appearance of amorphous material
Schedule prompt surgical evaluation
Rh negative: administer 250 IU anti-D immunoglobulin s/p surgical evacuation
Pt to f/u s/p surgical evacuation for serial beta-hCG on days 1, 7, 14, and 21
Prescribe combined hormonal OCP during f/u provided no contraindications exist
Second and Third Trimester Bleeding
Placenta previa
Pt with h/o placenta previa before 20 WGA presents with late-pregnancy painless vaginal bleeding. Denies recent placement of object(s) in vagina. VSS. Bright red blood per os observed on speculum exam; no cervical abnormalities noted.
Obtain CBC, fibrinogen, PT, PTT, blood type, antibody screen; G/C if delivery is not imminent
Obtain fetal NST
U/S to evaluate for placenta within 2cm of internal cervical os at > 28 WGA
<37 WGA with preterm contractions; administer tocolytic
<34 WGA with preterm contractions; administer corticosteroids
Repeat U/S at 36 WGA to determine appropriate mode of delivery and r/o placenta accreta due to previous c-section
Perform amniocentesis at 36-37 WGA to document pulmonary maturity
Pelvic rest advised
Placental abruption
Pt with h/o HTN, thrombophilia, tobacco/stimulant abuse presents with late-pregnancy vaginal bleeding and abdominal pain. Denies recent placement of object(s) in vagina. VSS. Bright red blood per os observed on speculum exam; no cervical abnormalities noted.
Obtain CBC, fibrinogen, PT, PTT, blood type, antibody screen; G/C if delivery is not imminent
Obtain fetal NST
U/S to evaluate for blood between placenta and myometrium
Rh neg.; Kleihauer-Betke test and administer Rhogam
<34 WGA with minor abruption; administer tocolytic, corticosteroids
Pt to be admitted for chronic monitoring if abruption recurs
Pt advised to stop tobacco/stimulant use
Vasa previa
Pt with late-pregnancy painless vaginal bleeding that started s/p SROM. Denies recent placement of object(s) in vagina. VSS. Bright red blood per os observed on speculum exam; no cervical abnormalities noted.
Obtain CBC, fibrinogen, PT, PTT, blood type, antibody screen; G/C if delivery is not imminent
Obtain fetal NST; if reassuring, analyze vaginal vault blood for fetal cells/hemoglobin (Apt test)
U/S to evaluate for vasa previa
Screen for vasa previa at 37-38 WGA during future pregnancies
Postpartum Hemorrhage
Pt with h/o coagulopathy presents with > 500mL EBL s/p vaginal delivery. Poor uterine tone, trauma, non-intact placenta noted on exam.
Obtain 16 gauge IV access; administer LR at 2:1 ratio of EBL
Initiate fundal message, Pitocin 40 IU/L IV
Cytotec (misoprostol) 1000mg rectally
No h/o asthma: Hemabate/Carboprost (15-methyl PGF2 alpha) 250mcg; repeat q15min, max 8 doses
No HTN: Methergine 0.2mg IM; repeat q2-4 hours
If bleeding continues despite medical therapy, obtain STAT labs with coags & fibrinogen; call blood bank and OB service