Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism
History
Presenting symptoms (sudden onset)
PE: Dyspnea, cough, hemoptysis, chest pain
DVT: Unilateral leg swelling/edema, calf pain
OR > 10 if within previous 3 months: Hip/leg fracture, spinal cord injury, cesarean section or surgery requiring general anesthesia,
OR 2-9: Pregnancy, estrogen therapy, central venous line, arthroscopic knee surgery
OR < 2: Immobilization (bedrest) due to illness/injury for 3+ days, prolonged travel in motor vehicle, varicose veins
Persistent risk factors (OR 2-9): Morbid obesity, heart failure, inherited thrombophilia, active cancer within previous 6 months +/- chemotherapy
Physical exam
Vitals (PE): Heart rate > 100 BPM, tachypnea, hypoxemia
DVT: Unilateral calf redness, warmth, swelling/edema, tenderness
Initial diagnostics
CBC, BMP
EKG: Precordial T-wave inversion, RBBB, S1-Q3-T3 suggesting PE
Less than 2: Calculate PERC and if ≥ 1, obtain d-dimer to rule out PE
Greater than or equal to 2:
Obtain lower extremity DVT ultrasound
No history of pulmonary HTN, heart failure: CT-angiography if lower extremity DVT is negative
Confirmed PE and/or DVT
Persistent shock including hypotension: Consider thrombolysis
Platelets > 70,000 with low hemorrhage risk and no limb ischemia, liver disease, ESRD, concerns for follow up:
Anticoagulation regimens
No morbid obesity and no current pregnancy/malignancy with weight > 60 kg and Cr < 1.5: Apixaban 10 mg BID x 7 days followed by 5 mg BID
Elevated bleeding risk: Start concomitant LMWH/warfarin x 5 days. Continue warfarin and titrate to INR 2-3.
Hemodynamically unstable with high bleeding risk, renal insufficiency, and/or morbid obesity: Start unfractionated heparin
First event
Provoked with immediately reversible risk factor: 3 months
Provoked with persistent risk factor (e.g. immobility, pregnancy): 3 months and consider extending to up to 12 months
Unprovoked and not a candidate for indefinite anticoagulation: 3 months
Repeat event: Initiate indefinite anticoagulation
IVC filter: Consider for patients who are not candidates for anticoagulation or fail anticoagulation
Counseling: Patient informed that s/he may develop post-thrombotic syndrome, venous ulcers
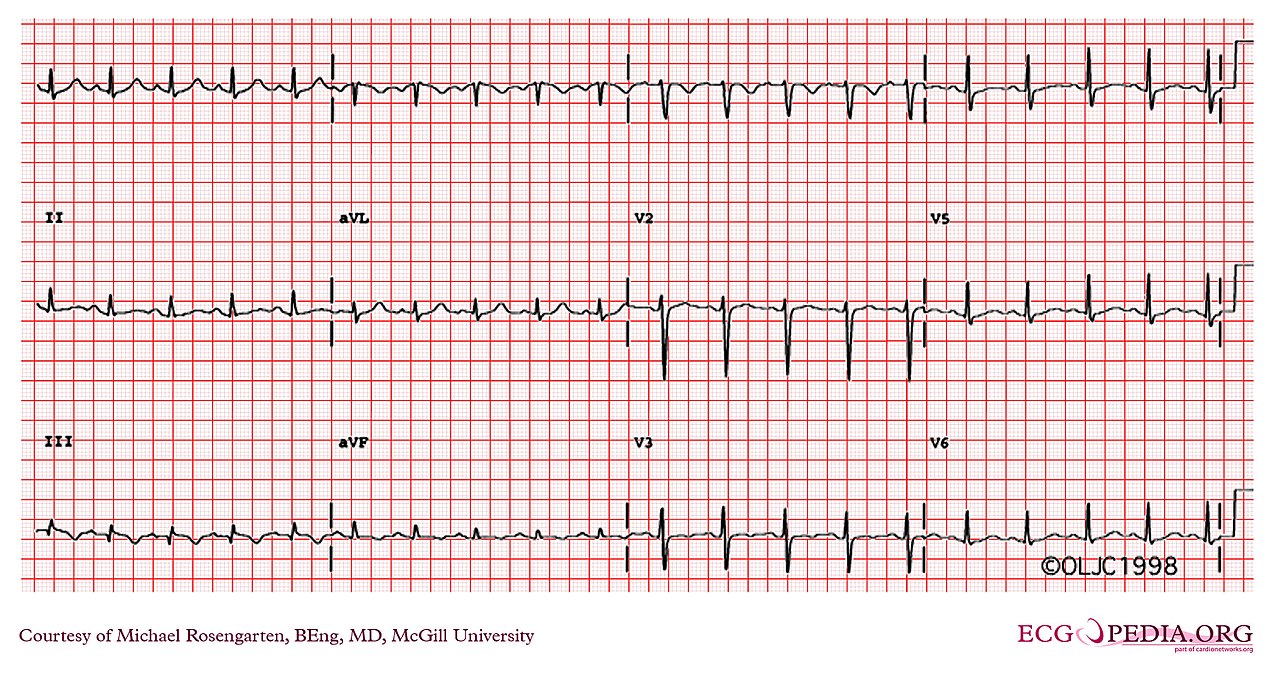
Right bundle branch block due to PE
Notes
Wells’ Criteria
DVT and PE risk factors: Previous DVT, active cancer during previous 6 months, immobility for > 3 days
DVT risk factors: Major surgery during previous 3 months
PE risk factors: Previous PE, major surgery during previous month
S1Q3T3
S wave in lead I, Q wave in lead 3, inverted T wave in lead 3
S wave = downward deflection after QRS complex (similar to a Q wave, but after the QRS)
Rarely seen in PE EKGs
Anticoagulation
Should not exceed 3 months if a reversible provoking factor/etiology is identified (see Wells’ criteria above)
Lovenox should be continued in patients with active malignancy
Apixaban
Selected over rivaroxaban in this vignette because rivaroxaban must be taken with food
Apixaban reduce dosing applies to patients who meet two of the following criteria: Age > 80 years, weight < 60 kg, serum creatinine > 1.5