Hypothyroidism
Primary Hypothyroidism
49 y/o F with h/o HTN, hyperlipidemia, recurrent miscarriages presents with chronic fatigue and cold intolerance. Reports h/o autoimmune disease, ovulatory/menstrual dysfunction, and neck irradiation. Denies currently being pregnant. ROS positive for poor concentration, depression, and diffuse muscle pain. Medications include amiodarone and lithium. Hair thinning, goiter, proximal muscle weakness, lower extremity edema, dry skin, and delayed deep tendon reflexes on exam.
TSH > 10 mIU/L with low free T4
Start levothyroxine 1.6 mcg/kg/day PO and repeat TSH testing in 6 weeks
Adjust levothyroxine dose every six weeks until TSH within reference range
Levothyroxine counseling
Take every morning on an empty stomach at least 30 minutes before food
Do not take within 4 hours of calcium, iron, and/or bile acid sequestrants (e.g. cholestyramine)
Notes
Initial workup
Fatigue and cold intolerance are the most common symptoms of hypothyroidism
May be preceded by signs/symptoms of hyperthyroidism, i.e. Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. In these cases, autoimmune destruction of the thyroid gland leads to chronic hypothyroidism.
Amiodarone and lithium may cause thyroid dysfunction
Start with TSH testing
General reference range is 0.5 < TSH < 10 mIU/L
If TSH > 5.5 mIU/L, obtain free T4
Treatment
TSH < 10 mIU/L and normal free T4 indicates subclinical hypothyroidism (see vignette/chart below)
Hypothyroidism treatment depends on age, symptoms, and pregnancy status
For patients 50 or older, start levothyroxine 25 mcg daily and increase by 25 mcg every 4 weeks until TSH reaches desired range
In newly pregnant patients, increase current levothyroxine from 7 to 9 tablets weekly (e.g. two tablets on Tuesday/Thursday and one tablet as usual on other days)
TSH changes in previously stable hypothyroid patients being treated with levothyroxine:
Numerous medications may alter TSH, including SSRIs
Decreased levothyroxine absorption may occur with atrophic gastritis, chronic PPI use, and/or H. Pylori infection
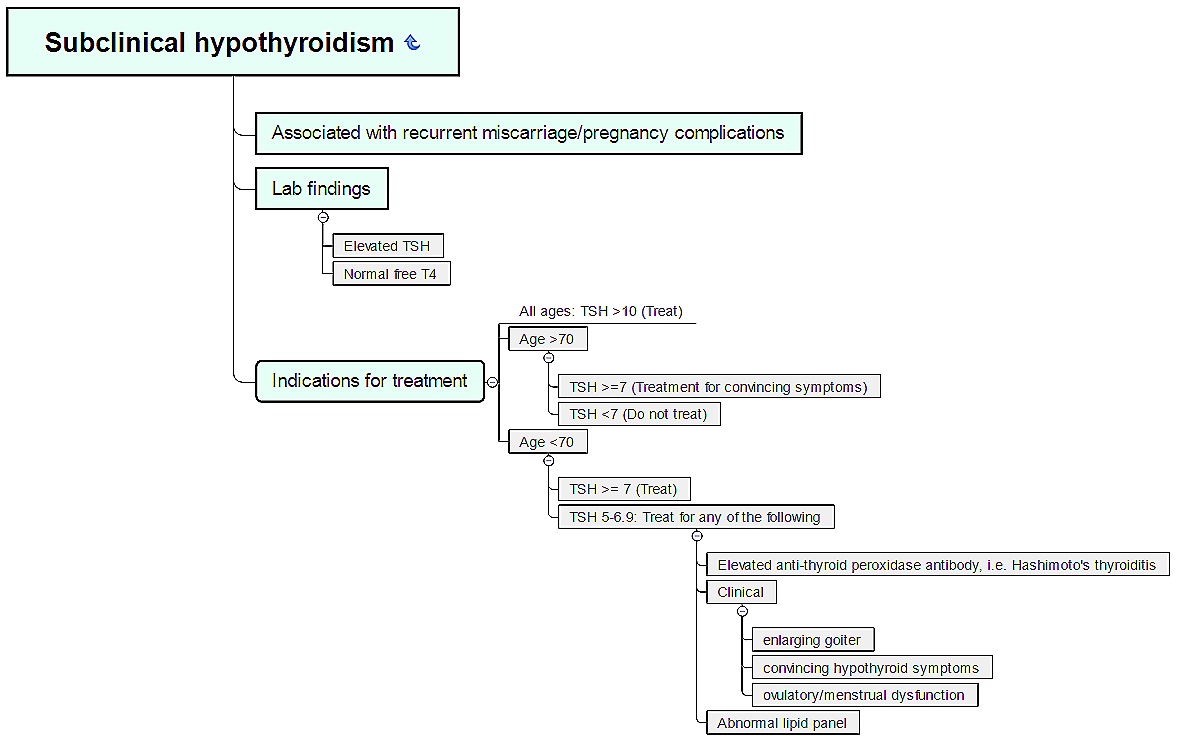
Subclinical Hypothyroidism
69 y/o F with h/o autoimmune disease and neck irradiation presents with chronic fatigue and cold intolerance. Denies weight gain, constipation, arthralgias/myalgias, weakness, difficulty concentrating, depression. Vital signs WNL. Normal hair, thyroid, and skin on exam.
TSH 6.9 mIU/L with normal free T4
Obtain lipid panel, anti-thyroid peroxidase antibodies
Treat as indicated per laboratory results
Notes
Subclinical hypothyroidism = elevated TSH with normal free T4
Treatment depends on age, symptoms, TSH, anti-TPO antibodies, and lipid panel (see below)
Rule of 7’s: TSH 7 mIU/L or greater and
70+ y/o = treat if symptomatic
Less than 70 y/o = treat