Pediatrics
Newborn
USPSTF Recommendations
≥ 6 months: Oral fluoride supplementation if water supply is fluoride deficient
6 months to 24 years with fair-skin: Counsel about UV radiation, skin cancer, and sunscreen use
3 to 5 years: Vision screening for amblyopia, vision loss
≥ 6 years and obese (≥ 95th percentile): Offer intensive behavioral interventions to promote improvements in weight status
≥ 12 years: Depression screening
≥ 15 years: Screen for HIV
Sexually active
Counsel about risk for STIs
High risk activity: Screen for hepatitis B, syphilis and offer PrEP therapy
Females ≤ 24 years: Screen for gonorrhea/chlamydia. Adult recommendations concerning intimate partner violence screening, folic acid supplementation apply.
Well Child Check
Cow’s milk recommendations
< 1: No cow’s milk
1-2 years: 8 oz whole milk daily
2-8 years: 16 oz 2% milk daily
8-18 years: 24 oz 2% milk daily
Sleep recommendations (per day) ≈ (14 - age in years) hours/day until 4 years old and then ≥ 10 hours/day until a teenager
4-12 months: 12-16 hours
1-2 years: 11 to 14 hours
3-5 years: 10-13 hours
6-12 years: 9-12 hours
13-18 years: 8-10 hours
Eye deviation: Refer to ophthalmology at age 6 months
Vitamin supplementation until age 6 months for breastfed infants
Vitamin: 400 IU/day
Iron 1 mg/kg/day
Fluoride supplementation for deficient water supplies
0 to 6 months: None
6 months to 3 years: 0.25 mg/day
3 to 6 years: 0.5 mg/day
6 to 16 years: 1 mg/day
Influenza vaccine
Age
6 months to 2 years: Inactivated vaccine
2 to 18 years: Live attenuated vaccine
18 years and older: Recombinant vaccine
One vs. two doses: Any child 8 years or younger who has received < 2 lifetime doses: Administer first dose now followed by 2nd dose in 4 weeks
Additional Resources
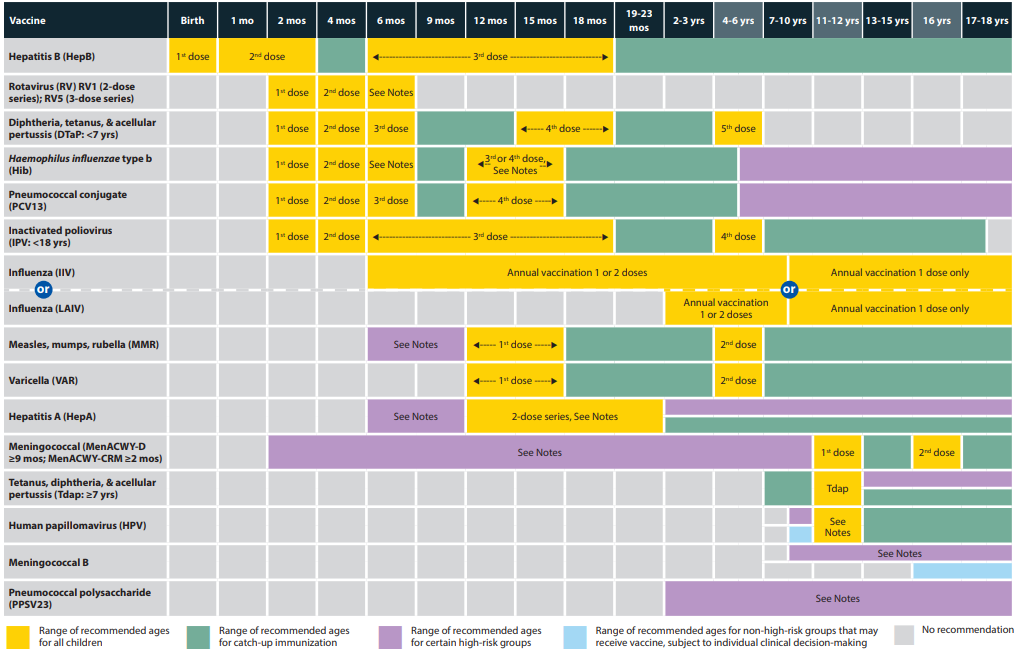
CDC: Milestone assessment and pediatric vaccination schedule
General Assessment
For Parents: Toilet training and a resource for providers/parents (Katherine Osman, editor Giselle May)
Note Templates and Bright Futures Handouts
2 year
Bright Futures 2 year handout
2.5 year: See Bright Futures Pocket Guide
3 year
Bright Futures 3 year handout
4 to 5 years
6 to 8 years
11 to 12 years: See Bright Futures Pocket Guide
12 to 18 years: See Bright Futures Pocket Guide
A Guide for Office Vaccines
Pediatric influenza vaccination guidelines for children age 6 months through 8 years. Source: DCDC Prevention and Control of Seasonal Influenza with Vaccines: Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices—United States, 2018–19 Influenza Season.
A Guide for Office Vaccines
Vaccine Memorization
Number of doses
4 dose = P vaccines (PCV13, Polio)
5 dose = DTap (D is the Roman numeral for 500)
2 dose = HAMMR Varicella at 1 (all), 2 (Hep A), and 4 years (MMR, varicella)
Last doses
6 months = Hep B and rotavirus
1 year = PCV 13 and HIB
4 years = Polio and DTaP
Individual vaccines
Influenza (Fluzone Quad)
Ages 6 to 35 months: Administer 0.25 mL
Age 36 months or older: Administer 0.5 mL
See algorithm (right) for information concerning the administration of 1 versus 2 doses in children younger than 9 years
HPV: Administer 1 dose at the 11 and 12 year old well child checks
The meningococcal B vaccine is CDC approved, but not mandatory