Hypertension Management per JNC 8
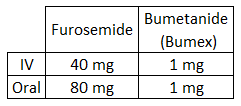
Oral Lasix Equivalents (OLE)
Thiazide Diuretics: Additional Information
Contraindicated if GFR < 30 (exception = metolazone)
Renal effects
Decrease excretion of
Calcium → reduced bone mineralization
Uric acid → increased gout
Lithium → increased toxicity
Increase potassium and magnesium excretion
Agents
HCTZ 12.5 and 25 mg daily produce similar decrease in BP
Chlorthalidone supported by ALLHAT and SPRINT trials
Secondary Hypertension
Common Etiologies
Potential contributing factors
Diet: Sodium
Substances: Caffeine, nicotine, alcohol, cocaine
OTC medications: NSAIDs, herbal supplements
Prescriptions: OCPs, steroids, EPO
Hyperaldosteronism
Most common pathophysiology
May be associated with hypoglycemia
Diagnose with aldosterone:renin ratio
Additional Considerations
Pediatric
Coarctation of the aorta: Obtain echocardiogram
Renal parenchymal disease: Obtain BMP, U/A, renal ultrasound
Adult
Renal artery stenosis
Risk factors: Age > 50 years, atherosclerotic disease, fibromuscular disease, smoking
May be associated with refractory heart failure, flash pulmonary edema, CKD (ischemic nephropathy)
Diagnosis: Renal artery ultrasound with Doppler (or MRA if inconclusive) shows > 60% luminal occlusion
Treat cardiovascular risk factors and evaluate for revascularization (e.g. transluminal renal angioplasty +/- stenting)
Endocrine: Hyperthyroidism, hypercortisolism, pheochromocytoma