Ankle/Heel/Foot Pain
Ottawa Ankle Rules
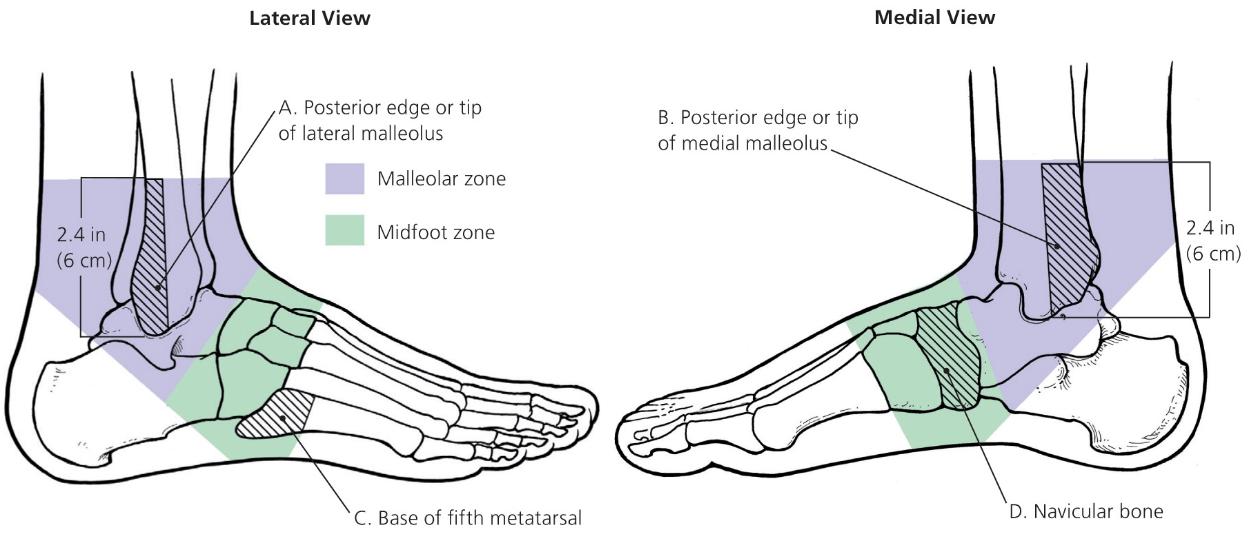
Ankle x-ray for pain in the malleolar zone and one of the following:
Inability to bear weight for four steps both immediately and in ED
Bone tenderness at the posterior edge or tip of the lateral and/or medial malleolus
Foot x-ray for pain in the malleolar zone and one of the following
Inability to bear weight for four steps both immediately and in ED
Bone tenderness at the navicular and/or base of the fifth metatarsal
Differential Diagnosis
Plantar warts. Source: Marionette.
Heel and Ankle Pain
Adult
Plantar
Plantar warts: Raised skin lesions associated with pain on palpation. Lesion shaving, topical salicylic acid, imiquimod cream, and/or cryotherapy. Consider referral to podiatry for surgical excision. Duct tape is ineffective.
Plantar fasciitis (most common etiology): Sharp/aching anterior heel pain worse with weight bearing following rest. NSAIDs, stretches, night splinting, physical therapy. Consider corticosteroid injection, platelet rich plasma injection, extracorporeal shock wave therapy for recalcitrant cases.
Often confused with plantar fasciitis:
Heel pad syndrome: Deep mid-heel ache in worse with prolonged walking. NSAIDs, RICE, weight loss. Rigid heel cup. Consider podiatry referral.
Calcaneal stress fracture: Sudden increase in activity with minimalist shoes followed. Pain worse in the morning and with ambulation.
Medial
Tarsal tunnel syndrome: Almost always occurs following clear foot trauma
Intermittent numbness and aching/burning medial/plantar foot pain worse at night and with prolonged walking
Pes planus, pain with ankle dorsiflexion/eversion, positive triple compression test
Ankle x-ray to rule out dislocation/fracture of talus, calcaneus, and/or medial malleolus; consider bilateral EMG to compare affected and unaffected foot
NSAIDs, shoe modifications, and/or orthotics; consider corticosteroid injection vs. nerve decompression surgery for recalcitrant cases
Eccentric calf strengthening exercises (video) for achilles tendinopathy
Lateral
Lumbar radiculopathy
Posterior
Achilles tendinopathy
Middle-age distance runners with posterior pain and palpable achilles tendon nodule
NSAIDs and eccentric calf strengthening exercises; consider extracorporeal shock wave therapy for recalcitrant cases
Do NOT treat with corticosteroid or platelet-rich plasma injections
Reference: British Journal of Sports Medicine
Additional Considerations
Neuroma
Neuropathy
Inflammatory
Acute: Gout
Chronic: Rheumatoid arthritis, fibromyalgia
Infectious
Diabetic foot ulcers: Stage per university of Texas System (Table 1). Address peripheral vascular disease, glycemic control, neuropathy. MRI if concern for osteomyelitis. Antibiotics if infected. Podiatry for debridement and pressure relief/offloading recommendations. Wound care consult and follow-up outpatient.
Pediatric
Fracture: Two-view (lateral/axial) plain film
Calcaneal apophysitis (Sever's Disease)
Elementary/adolescent athlete s/p "growth spurt"
Tenderness with compression of mediolateral posterior calcaneus
NSAID, RICE, stretching, 3 to 6 weeks rest
Achilles tendonitis: Tendon inflammation in adolescent athlete
Foot Pain/Discomfort
Acute
Stress fracture: Pain with walking following sudden increase in physical activity
Plain film and consider MRI to rule out 5th metatarsal fracture
Crutches (4 days) → boot (4 weeks) → re-evaluation → rigid shoe (4 weeks)
Acute limb ischemia (embolism)
Subacute and/or chronic
Plantar wart (see above)
Poikilothermia (cold feet): Raynaud’s phenomenon, atherosclerosis (peripheral arterial disease), neuropathy
Toe Pain
Toe fracture: Plain radiograph with anteroposterior, lateral, and oblique views
Gout: Excess meat/liver/beer/high-fructose corn syrup, loop/thiazide diuretic
Calculate acute gout diagnosis rule and CrCl per BMP. Definitive diagnosis with with aspiration.
Indomethacin (CrCl > 30) vs. colchicine (CrCl < 30).