Shoulder Pain
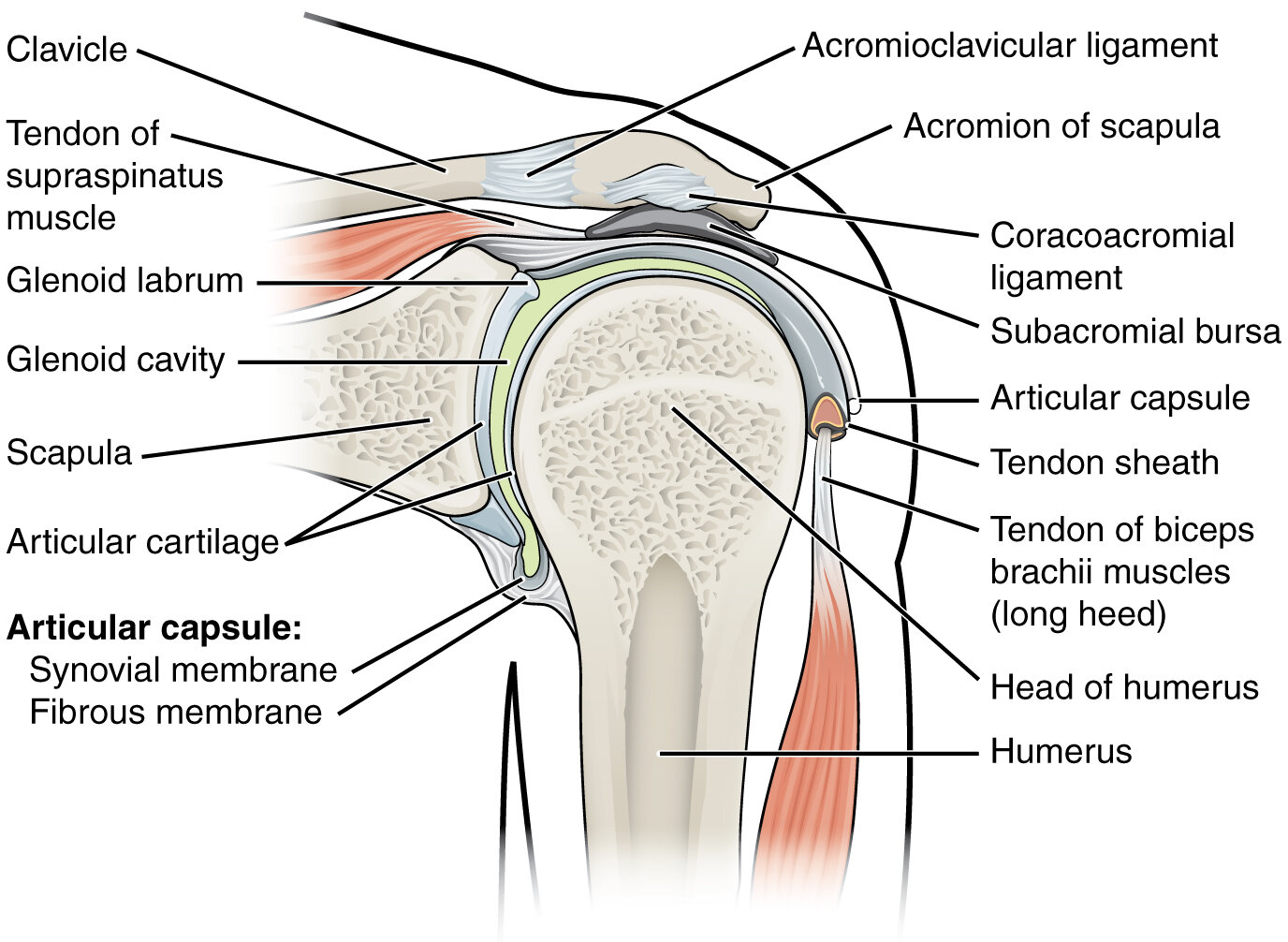
Shoulder anatomy. By OpenStax College.
Referred pain distribution. By OpenStax College - Autonomic Reflexes and Homeostasis.
Differential Diagnosis
Acute Pain (Obvious/Emergent)
Clavicle
Acromioclavicular injury
Clavicle fracture
Glenohumeral dislocation
Proximal humerus fracture
Less common: Referred shoulder pain
Left shoulder/arm: Cardiac involvement, e.g. pericarditis, myocardial infarction
Right shoulder: Hepatobiliary, e.g. gallstones, pancreatitis
Intra-abdominal hemorrhage (rare): Phrenic nerve (diaphragm) irritation referred to C5, e.g. pneumonia, perforated peptic ulcer, ruptured ovarian cyst/ectopic pregnancy
Acute or Chronic Pain
Superior labral tear from anterior to posterior (SLAP) tear
Thoracic outlet syndrome (less common): Compression of vessels/nerves by clavicle produces referred numbness/pain when arms are lifted to shoulder level. Arm weakness and numbness may be present on exam. Refer to physical therapy and consider surgery for refractory cases.
Chronic Pain
Common
Shoulder pathology
Cervical radiculopathy
Less common
Calcific tendonitis
Shoulder arthritis: Rare without history of shoulder trauma
Acromioclavicular arthritis
Glenohumeral osteoarthritis
Autoimmune (rare)
Shoulder Exam
Assess for musculoskeletal instability from front, side and back
Palpate clavicle and acromioclavicular joint
Assess for muscle tenderness and instability
Sulcus sign: Indicates shoulder instability
Test range of motion:
Abduction (jumping jack)
Adduction (X across the body)
Elevation through forward flexion (judo chop without bending elbow)
Extension (swan dive)
External rotation (robot arms rotate outward): Decreased ROM or pain indicates adhesive capsulitis
Internal rotation (back scratch with the thumb)
Rotator cuff
Empty can test (supraspinatus): Patient holds arms directly in front and pretends to empty two cans
Neer test (subacromial impingement): Place fully pronated arm in forced flexion
Hawkins-Kennedy (supraspinatus impingement syndrome): Arm bar and rotate downward
External lag (infraspinatus/teres minor): Resistance against external rotation and/or inability to hold arm in external rotation
Internal lag/Gerber Lift-off (subscapularis)
Resistance against internal rotation
Place hands behind back and lift off with/without resistance
Biceps tendon and labral/SLAP tear
Physical exam
Speed test: Straight arm with palm up “asking for candy”
Crank test: Indicates labral/SLAP tear, especially if Speed test is positive
Note: Physical exam for a biceps tear can be unreliable. If suspected, obtain an MRI of the elbow for definitive diagnosis.