Labs and Imaging
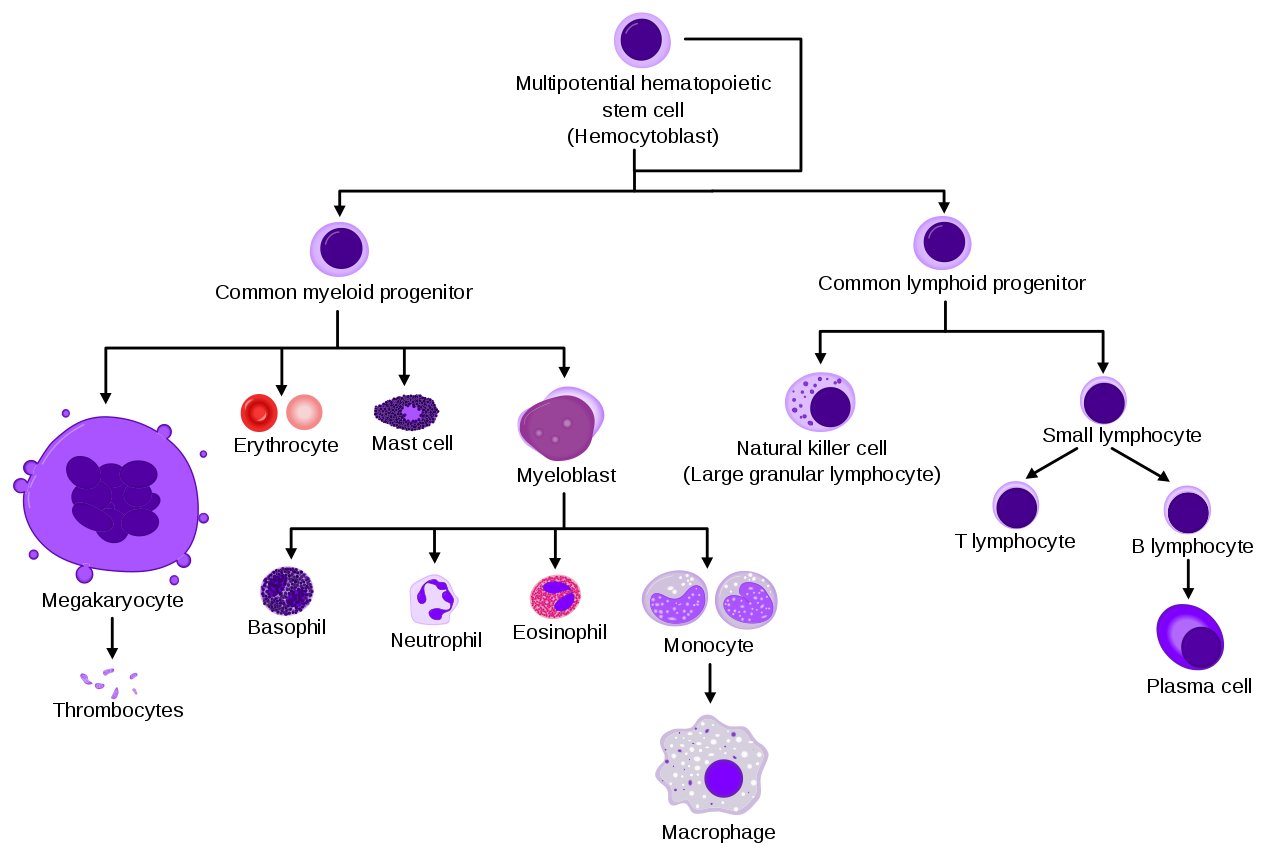
WBC
Acute myelogenous leukemia
Anemia
Microcytic
Anemia of chronic disease
Thalassemia
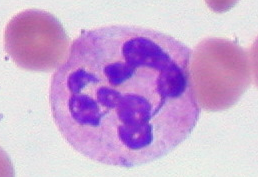
Hypersegmented neutrophil, i.e. ≥ 5 lobes present. Pathological and histological images courtesy of Ed Uthman.
Normocytic
Hemolytic
Adult: Autoimmune hemolytic disease
Patients age > 40 years
Pathophysiology: Cold-reactive antibodies formed in response to EBV or mycoplasma infections
Pediatric
DDX: Sickle cell disease, spherocytosis, G6PD deficiency
Obtain CBC, corrected reticulocyte index, peripheral blood smear, +/- hemoglobin electrophoresis
Non-Hemolytic
Pediatric: Aplastic crisis, transient erythroblastopenia of childhood
Macrocytic
Megaloblastic anemia (hypersegmented neutrophils): B12/Folate deficiency
Non-megaloblastic anemia (neutrophils with < 5 lobes)
Alcohol-use disorder
Pediatric (rare): Blackfan-Diamond syndrome
Platelets
Consider HIT, TTP/HUS, ITP, DIC
BMP/CMP
Individual Values
Sodium: Hyponatremia, hypernatremia
Potassium
Hypokalemia
Common etiologies: Vomiting, diarrhea, bulimia nervosa
Less common etiologies: Dialysis/plasmapheresis, VIPoma
Medication-induced: Diuretics, laxatives, insulin, albuterol
Hyperkalemia (consider if K+ > 5.5, start if > 6)
Calcium gluconate 1000 mg (10 mL of 10% solution)
Albuterol nebulizer q4-6 hours
Regular insulin 10 u in 500 mL 10% dextrose solution
Potassium binder: 8.4 g qd (onset of action = 7 hours)
Consider nephrology consult
Chloride
Bicarbonate
Low
Unstable: Obtain CBC, CMP, serum lactate, ABG, UDS and consider beta-hydroxybutyrate in setting of hyperglycemia
Stable: Obtain CBC, CMP serum albumin and calculate anion gap (Na − [Cl + HCO3]); see acid-base disturbances for further information
BUN and Creatinine
Elevated creatinine (Cr)
Acute kidney injury (≥ 1 of the following): Cr ≥ 1.5x baseline, Cr ≥ 3.0 mg/dL, urine output < 0.5 mL/kg/h for 6-12 hours
Hyperglycemia
Diabetes mellitus: Type 1 and Type 2
Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state (HHS)
Hypoglycemia: Neonatal hypoglycemia
Elevated serum protein: Consider serum protein electrophoresis
Hypogammaglobulinemia: Indicates immunodeficiency
Primary: Congenital (pediatric)
Secondary: Metabolic (renal disease, DM), loss in urine/stool, malignancy, immunosuppression (HIV, Rx)
Hypergammaglobulinemia
M-protein negative: Liver disease, autoimmune disease, chronic infection, malignancy
M-spike positive: MGUS (no lytic lesions), multiple myeloma (lytic lesions), Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia (monoclonal IgM, Bence-Jones protein)
Liver enzymes (acute elevation)
Review risk factors: Recent travel, alcohol use, IV drug use, sexual history, medications. Discontinue offending agents (e.g. statins).
Review of systems: Ischemia risk (e.g. CAD, mesenteric ischemia), coagulopathy risk (e.g. previous DVT/PE), abdominal pain, jaundice
Obtain: Hepatitis A Ab/IgM, HBSAg, anti-HBs, anti-HBc, albumin, bilirubin, alkaline phosphatase (+/- GGT), PT, PTT, INR
Value Patterns
Liver enzymes
Hepatocellular
NAFLD
Alcohol-induced liver disease (AST:ALT > 2)
Other: Autoimmune, cholestatic, infiltrative
Urinalysis
Proteinuria: Chronic kidney disease, nephrotic syndrome
Other
Hypertriglyceridemia
Hepatitis panels: Hepatitis B, hepatitis C
PTH
High (hyperparathyroidism): Primary and secondary
Imaging
Conditions
Modality
Source: Colorectal Cancer Screening and Surveillance per AAFP. Memory device: Tubular adenomas < 10 mm divided by 2 (or fewer) polyps = 5 years.